
Exploring the Wonders of the Lunar Eclipse Tonight

Introduction to the Lunar Eclipse
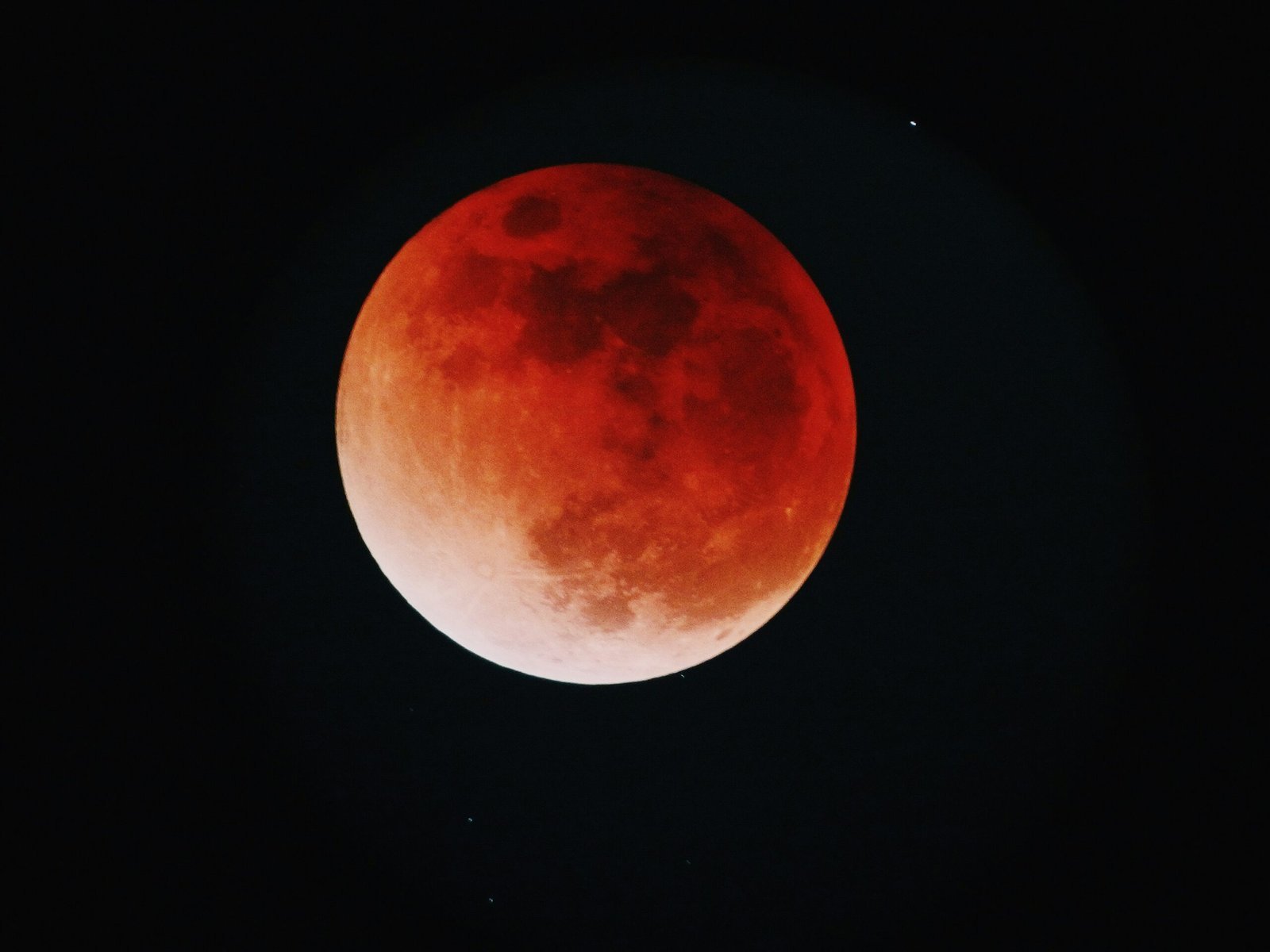
A lunar eclipse is a celestial event that occurs when the Earth passes directly between the Sun and the Moon, causing the Earth’s shadow to obscure the Moon. This alignment results in the Moon being temporarily darkened, showcasing a remarkable demonstration of the dynamic relationships between these three astronomical bodies. There are different types of lunar eclipses, including total, partial, and penumbral, each distinguished by the extent to which the Earth’s shadow covers the Moon. Total lunar eclipses are particularly captivating; during these events, the Moon can take on a reddish hue, earning it the moniker “Blood Moon” due to the scattering of sunlight through the Earth’s atmosphere.
The phenomenon occurs approximately three times a year, with some years featuring fewer or more events depending on the alignment of the Sun, Earth, and Moon. For a lunar eclipse to take place, the timing must be just right; it generally happens during a full moon when the Moon is positioned on the opposite side of the Earth from the Sun. During this time, the Moon passes through the Earth’s shadow, which consists of three parts: the umbra, penumbra, and antumbra. The umbra represents the darkest part of the shadow where totality occurs, while the penumbra is the lighter outer shadow, enabling partial eclipses.
For both casual observers and dedicated astronomy enthusiasts, lunar eclipses serve as extraordinary opportunities to explore the night sky. These events are not only visually stunning but also an excellent moment for educational outreach, as they provide a relatable way to engage with astronomical concepts and foster a greater appreciation for the wonders of our universe. The spectacle of watching the Moon transition through various phases of shadow highlights the intricate choreography of celestial mechanics, drawing interest from a wide array of viewers around the globe.
The Science Behind Lunar Eclipses
Lunar eclipses occur when the Earth positions itself directly between the sun and the moon, resulting in the Earth’s shadow casting a barrier over the lunar surface. This celestial event consists of three primary phases: the penumbral, partial, and total lunar eclipse, depending on the alignment and the degrees of shadow coverage experienced by the moon. During a penumbral eclipse, the moon only passes through the outer shadow of the Earth, known as the penumbra. This phase may go unnoticed as the moon darkens subtly. In contrast, a partial lunar eclipse happens when only a portion of the moon enters the darker region of Earth’s shadow, or umbra, allowing observers to detect a clear shadow across the moon’s surface.
The total lunar eclipse is perhaps the most dramatic, as the entirety of the moon travels into the Earth’s umbra, resulting in a vivid reddish hue. This coloration occurs due to Rayleigh scattering, a phenomenon similar to why sunsets appear red. As sunlight passes through the Earth’s atmosphere, shorter blue wavelengths are scattered out, while the longer red wavelengths are bent toward the moon, creating a remarkable optical effect that captivates onlookers. The precise alignment of the sun, Earth, and moon necessary for a total eclipse does not happen frequently, as the moon’s orbit is slightly tilted in relation to Earth’s orbit around the sun.
Understanding the science behind lunar eclipses enhances our appreciation for these celestial events, as it reveals the intricate dance of these solar and lunar bodies. As we observe a lunar eclipse, we witness a fusion of physics and astronomy, illustrating the fascinating dynamics that govern our solar system. Observing the interplay of shadows and light during a lunar eclipse serves as a reminder of the complex and beautiful relationships between celestial entities. This understanding deepens our engagement and enhances our experience as we gaze at the illuminated moon amidst the backdrop of a darkened sky.
Types of Lunar Eclipses
A lunar eclipse occurs when the Earth passes between the sun and the moon, casting a shadow on the lunar surface. There are three main types of lunar eclipses: total, partial, and penumbral. Each type offers a unique observation experience and varying visual characteristics that inspire awe among enthusiasts and casual observers alike.
A total lunar eclipse is the most dramatic of the three. During this event, the Earth’s shadow completely covers the moon, often resulting in a striking reddish hue, commonly referred to as a “Blood Moon.” This coloration occurs due to Rayleigh scattering, where shorter blue wavelengths of light are scattered out by the Earth’s atmosphere, leaving the longer red wavelengths to illuminate the moon. Observers are typically treated to an extraordinary sight as the moon transitions through different shades of red, creating a mesmerizing display that can last for several hours.
In contrast, a partial lunar eclipse occurs when only a portion of the moon enters the Earth’s shadow. This results in a distinct shadowed section that contrasts sharply with the sunlit part of the lunar surface. Observers can note the curvature of the Earth’s shadow, which provides visual evidence of the planet’s round shape. Partial eclipses can be captivating; they often unfold gradually as the shadow advances across the moon, allowing observers to witness the transition smoothly.
Lastly, the penumbral lunar eclipse is the least dramatic type. In this case, the moon passes through the Earth’s penumbral shadow, resulting in subtle shading that may be difficult to detect without careful observation. During a penumbral eclipse, the moon might appear slightly darker, but the changes are not as striking as those in total or partial eclipses. While they are often overlooked, penumbral eclipses still hold value for dedicated enthusiasts looking to study the nuances of lunar appearances.
Tonight’s Lunar Eclipse: Timing and Visibility
The lunar eclipse occurring tonight is a celestial event that captivated stargazers and astronomy enthusiasts alike. A lunar eclipse happens when the Earth moves directly between the Sun and the Moon, projecting its shadow onto the Moon. This phenomenon will take place in several stages, each with its own distinct characteristics and timings.
The eclipse will commence at approximately 8:00 PM UTC when the penumbral phase begins. During this stage, the Moon will start to glide into the penumbra, the outer part of Earth’s shadow. Although this phase is subtle, it marks the beginning of the lunar eclipse where observers may notice a slight shading on the Moon’s surface. The partial eclipse will follow at around 9:30 PM UTC, marking a more pronounced shadow that obscures part of the Moon, transforming its appearance. The maximum eclipse will occur at 10:00 PM UTC, where the Moon will appear at its darkest, creating a spectacular sight for viewers.
Regions across North America, parts of South America, Western Europe, and some parts of Africa are anticipated to have excellent visibility during this occurrence. Observers in these regions can enjoy unobstructed views of the lunar eclipse provided weather conditions are favorable. However, those in other parts of the world may encounter some challenges due to local weather or geographical factors such as mountains or tall buildings that could obstruct their line of sight.
It is advisable for enthusiasts to seek locations that offer a clear horizon. Moreover, using binoculars or a telescope can significantly enhance the viewing experience, allowing observers to appreciate the intricate details on the Moon’s surface illuminated by the subtle light reflecting off it during the eclipse. Given these timings and visibility conditions, tonight’s lunar eclipse promises to be an event worth witnessing.
How to Observe the Lunar Eclipse
To fully appreciate the beauty and astronomical significance of a lunar eclipse, proper observation techniques are essential. The ideal way to observe this celestial event is to choose a location with minimal light pollution. Urban areas often carry excessive artificial lights, which can hinder the visibility of the eclipse. Therefore, heading towards rural areas or elevated locations can significantly enhance your viewing experience. Look for parks or natural spots where the sky is unobstructed by buildings and trees.
Equipping yourself with the right tools is equally crucial. While the naked eye is sufficient for viewing a lunar eclipse, binoculars or a small telescope can provide a more detailed and captivating perspective. Binoculars are often recommended for beginners due to their portability and ease of use, allowing you to see the moon and its phases in finer detail. A telescope, on the other hand, offers the ability to observe finer surface features or the surrounding celestial bodies, transforming your experience into a more immersive event.
When observing a lunar eclipse, one should also be aware of the timing and duration of the event, as these factors can vary significantly between different eclipses. Make sure to check local astronomical websites or apps for precise timings. Planning your observation time can elevate your experiences, such as setting up your equipment ahead of time to ensure you don’t miss the heightened dramatic moments as the earth’s shadow gradually covers the moon.
As you prepare for this awe-inspiring spectacle, remember to account for weather conditions. Clear skies are vital for optimal viewing, so track weather forecasts leading up to the event. Following these practical tips will help ensure that your lunar eclipse observation is both enjoyable and memorable.
Cultural Significance and Myths Surrounding Lunar Eclipses
Lunar eclipses have captivated human imagination for centuries, playing a prominent role in various cultures globally. These celestial events, where the Earth passes between the Sun and the Moon, casting a shadow that turns the Moon a reddish hue, have been interpreted through diverse mythological lenses. In many ancient civilizations, lunar eclipses were regarded as omens or portents. For instance, the Mesopotamians viewed these occurrences as indicators of royal fate, believing that a lunar eclipse might foreshadow the death of a king or an upheaval in governance.
Similarly, in ancient China, people feared that a lunar eclipse would signify the devouring of the Moon by a celestial dragon. To ward off this belief, festivities were often held, where the community would bang drums and pots to scare the dragon away. This cultural response illustrates how societal practices adapted around this cosmic event, intertwining fear and joy in the face of the unknown.
In Hinduism, lunar eclipses are considered inauspicious, and rituals are performed to purify oneself from the supposed negative influences during this time. The belief in the eclipse as a tainting phenomenon reflects a broader theme in many cultures, where the eclipse is associated with disruption or imbalance in the natural order. However, not all cultures interpret lunar eclipses negatively; some indigenous tribes view them as a time of reflection and renewal, aligning their spiritual activities with the cosmic alignment.
Moreover, myths and legends surrounding lunar eclipses have been passed down through generations, from the Greeks who personified lunar eclipses with the myth of Selene, the moon goddess, to various African traditions that regard the Moon as a symbol of fertility and change. Such a vast array of interpretations highlights the rich tapestry of human experience concerning celestial phenomena, demonstrating that lunar eclipses serve not only as scientific spectacles but also as significant cultural touchstones that resonate with humanity across time and space.
Fascinating Facts About Lunar Eclipses
Lunar eclipses have captivated humanity for centuries, and their unique characteristics have led to a wealth of fascinating facts. One notable aspect is that they are not rare events; on average, there are about two to four lunar eclipses each year. However, the occurrence of a total lunar eclipse—where the Earth completely covers the moon—adds an extra layer of intrigue. The last known historical total lunar eclipse occurred on January 20, 2019, and millions around the world witnessed its stunning reddish hue, often referred to as a “blood moon.”
Throughout history, various cultures have interpreted lunar eclipses differently. For instance, the ancient Greeks believed that a lunar eclipse signified the wrath of the gods, prompting various rituals to appease them. Similarly, the Mayans and other indigenous cultures often associated these celestial events with omens, influencing their agricultural practices and ceremonial occurrences.
From a scientific perspective, lunar eclipses provide valuable opportunities for research. During these events, shadows cast by the Earth on the Moon can reveal details about our planet’s atmosphere and its composition. The reddish appearance of the moon during a total lunar eclipse results from the Earth’s atmosphere scattering sunlight, which then filters through and illuminates the moon, a phenomenon that can be calculated and modeled by scientists.
Moreover, lunar eclipses have been recorded for thousands of years, with notable entries in ancient chronologies. The earliest recorded lunar eclipse occurred in 747 BC, documented by Assyrian astronomers. Such records assist modern scientists in understanding lunar cycles and improving our predictive models for future lunar eclipses.
In conclusion, lunar eclipses are not only a breathtaking astronomical experience but also a source of historical intrigue and scientific insight. Their regular occurrence and the rich tapestry of cultural interpretations make them a topic of lasting interest.
Photography Tips for Capturing the Eclipse
Capturing the beauty of a lunar eclipse presents a unique opportunity for photographers of all skill levels. The quiet elegance of the moon as it transforms under the Earth’s shadow can lead to stunning images when photographed correctly. To optimize your shots, it is essential to consider camera settings, composition techniques, and ways to enhance photo quality, particularly in low-light scenarios.
Firstly, when setting up your camera, utilize a tripod to maintain stability during exposure. Since lunar eclipses can take place over several hours, even the slightest movement can lead to blurring. For the best results, use a DSLR or mirrorless camera equipped with a telephoto lens, ideally between 200mm to 400mm. Adjust your aperture to a range of f/8 to f/11 for a sharper image. In terms of exposure settings, start with a shutter speed of around 1/125 second at ISO 100 to capture the moon’s details, and gradually adjust as the eclipse progresses. This adaptability is crucial, as the illumination will diminish as the event unfolds.
When it comes to composition, consider framing the moon with interesting elements in the foreground. Including a silhouette of trees, buildings, or even landscapes can provide context and depth to your photographs. Remember to be mindful of the rule of thirds; placing the moon off-center can create a more dynamic image.
Lastly, excellent photo quality during a lunar eclipse can be further enhanced with the use of post-processing techniques. Software applications enable photographers to adjust contrast, brightness, and color balance, which can bring out the moon’s characteristics and details. With the right preparation and skills, photographers can immortalize this celestial event in stunning clarity, making the most of this rare opportunity.
Conclusion: Embracing the Celestial Experience
The lunar eclipse represents a profound celestial event that captivates the imagination and curiosity of observers around the world. As the Earth’s shadow casts itself upon the moon, transforming its appearance into shades of copper and red, this spectacle reminds us of the intricate workings of our solar system. These occasions are not merely astronomical phenomena; they present an opportunity for learning and engagement with the natural world.
Throughout history, lunar eclipses have evoked a rich tapestry of myths and cultural significance. Many civilizations considered these events as omens or divine interventions, showcasing the powerful influence celestial bodies have had on human thought and creativity. In today’s modern era, we have the privilege to scientifically explore these occurrences, deepening our understanding of the universe. Observing a lunar eclipse allows us to connect with ancient traditions while also appreciating the scientific explanations behind this remarkable phenomenon.
It is essential to take a moment to appreciate the beauty and rarity of a lunar eclipse. These events don’t happen frequently, making each occurrence a sound reminder of the wonders that lie beyond our everyday lives. Engaging with family, friends, or the local community during a lunar eclipse fosters a collective appreciation of this celestial occurrence. Sharing observations and experiences enhances not only individual understanding but also enriches communal knowledge. Furthermore, photographs and shared narratives from such events can inspire others to look upwards and embrace the awe of our universe.
Hence, as the lunar eclipse illuminates the sky tonight, let it serve as a reminder to gather your loved ones, take time to observe this majestic event, and share your impressions. Embracing these celestial experiences can create lasting memories and foster a deeper connection to the wonders that the cosmos presents. Each eclipse serves as an invitation to explore the night sky, engage with its beauty, and nurture a sense of unity with the vast universe we inhabit.
Share this content:


Post Comment